Boundary Guards
M-Guard
XML Boundary Guard
M-Guard is an XML guard that is used at a network boundary to control traffic. An M-Guard instance is an application level data diode, with traffic flowing in one direction only. Commonly, M-Guard instances will be deployed in pairs, one controlling flow in each direction.
M-Guard takes inbound XML messages and either passes them through or blocks them. It does not perform any transformation; it expects correct messages and enforces correct behaviour.
M-Guard can be used by Isode and third-party applications. There are two primary deployment scenarios:
- Cross-Domain. When two secure domains communicate across a national of organizational boundary, it is often important to tightly control information flow across the boundary. M-Guard sits on the boundary to provide necessary controls and assurance.
- Red/Black separation. Secure systems are often split with a Red (internal/secure) and Black (external) side. Primary red-side data is always encrypted at the red/black boundary, typically with a Type 1 (NSA definition) type cryptographic system. There is often a need for management and control information to flow across the red/black boundary (crypto bypass). M-Guard is an appropriate device to control information flow across a red/black boundary.
At boundaries where simple firewall protection is insufficient, M-Guard can provide checks including:
- Prevent leak of sensitive data (e.g., by Security Label checks; sender/recipient checks)
- Prevent Covert Channels
- Prevent malware and attacks
- Encoding/Syntax/Schema checks
- Business Rule Checks
Further information is provided in the whitepaper [M-Guard: Isode’s XML Guard].
Application Integration
An M-Guard instance will sit between a pair of applications (producer and consumer), with XML messages flowing from producer to consumer. M-Guard, acting as an application level data diode, will validate messages and only pass through those that match configured criteria. These applications will be connected to the M-Guard appliance on separate networks.
M-Guard provides (optional) acknowledgement of transfer to enable reliable transfer from producer to consumer. There is no extra information included with the acknowledgement, to avoid creation of a covert channel.
When the producer application initiates a connection to M-Guard, then M-Guard will connect to the consumer application before accepting the inbound connection.
The protocol used by applications that communicate with M-Guard is the Guard Content eXchange Protocol (GCXP). Isode has published the GCXP protocol in Appendix B of the M-Guard Administration Guide. Isode has also provided a freely available C++ reference implementation of GCXP. Characteristics of GCXP:
- Transfers a stream of XML Messages.
- TLS is always used to protect the connection.
- Two way strong authentication is recommended to validate peers.
- M-Guard will always validate IP address of connecting application.
- Framing using RFC 7049 – Compact Binary Object Representation (CBOR).
Application Profiles
Each guard instance is configured with an Application Profile, which enforces basis protocol compliance to the protocol used by the application. The application profile also applies content normalization of the XML and Unicode to ensure only a single specified representation of the protocol is used. This guards against covert channels and attacks using encoding variants.
M-Guard allows import of application profiles and includes support of a generic XML profile and a profile for “Demo Protocol”. Demo Protocol provides a means to show a range of M-Guard capabilities, including support of security labels following XEP-0258 (Security Labels in XMPP) and NATO STANAG 4774/4778.
Application Profiles are discussed in more detail in the Isode whitepaper [XML Guard Application Profiles].
Rules & Rule Catalogs
M-Guard can apply a set of rules to check XML messages. A key benefit of using XML is that there are a wide range of standardized mechanisms to check XML messages. M-Guard supports rules using the following standards:
- XML Schema. Schema of the XML protocol.
- Xpath. A mechanism useful for specifying generic checks.
- Schematron. A flexible mechanism for specifying rules.
- Relax NG. A modern XML specification mechanism.
An application will typically have a set of Rule Catalogs. Rule Catalogs can be loaded into an M-Guard Project, and then rules from these Catalogs can be enabled for each Guard. Applications using M-Guard are expected to provide an appropriate set of Rule Catalogs.
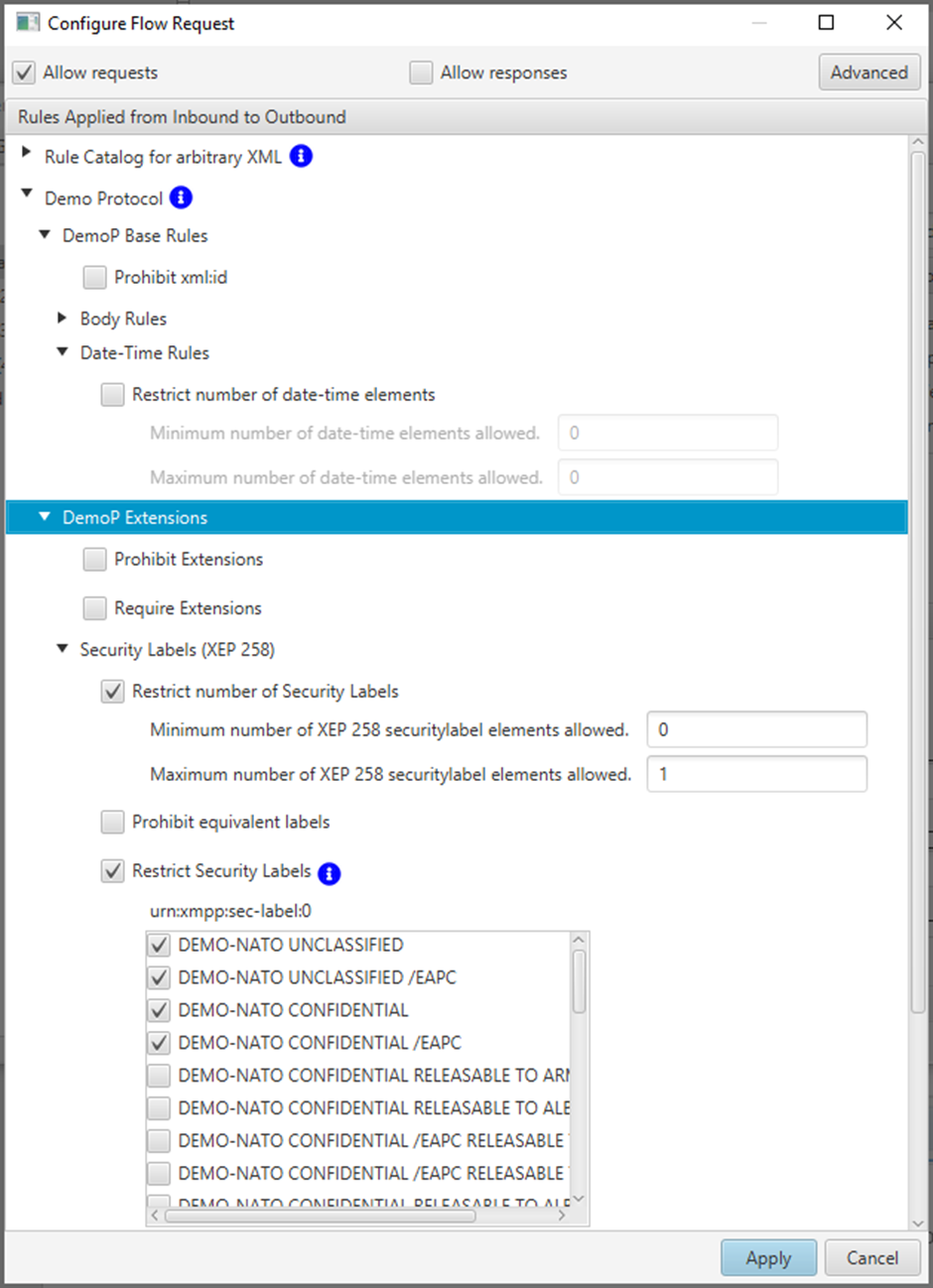
M-Guard supplies two Rule Catalogs with M-Guard Console that are shown above in the M-Guard Console UI:
- Demo Protocol Rules. These can be used with the Test Producer and Test Consumer to demonstrate M-Guard capabilities using the Demo Protocol. These rules show parameterization, where the M-Guard configuration includes parameters to constrain the rules.
- Rules for arbitrary XMP. These provide generic constraints, which can be used with arbitrary XML.
Rule may reference content catalogs, which are catalogs of arbitrary XML objects. M-Guard provides built in support for catalogs of XEP-0258 Security Labels and STANAG 4774/4778 NATO Confidentiality Metadata Labels.
Rate Limiting
M-Guard provides a mechanism to limit the rate of messages being sent through M-Guard to a configured value. When rate limiting is enabled, the guard will limit the rate at which messages are sent through the guard. This control may be used to reduce covert channel risks and/or Denial of Service risks, noting that its application may increase Denial of Service risk.
Cross-Domain Clock Synchronization
Where M-Guard is used to separate Red and Black systems, there is sometimes a need to synchronize clocks through the guard. One example is taking black side time information (perhaps from GPS) and using this to set clocks on red side systems. Another example is using a management network clock to set the clocks on red side systems, M-Guard provides a means to achieve this using Network Time Protocol (NTP).
Accreditation/Assurance
M-Guard is intended for environments where it will generally be required that the product used has undergone appropriate accreditation or assurance processes. M-Guard has been developed with processes and approaches to facilitate accreditation and assurance. It has undergone a UK assurance process.
M-Guard can be used with a wide variety of applications, including 3rd party applications, that use GCXP to communicate over M-Guard. Isode also plans to provide a number of applications that can be used with M-Guard or another XML Guard.
The first class of product uses M-Guard for red/black separation, there are three products:
- Icon-5066, Isode’s STANAG 5066 Server. M-Guard is used to support crypto bypass.
- Red/Black, a product which enables monitoring and control of black side devices (e.g., HF Radios and Antennae) with a Red Side Web UI.
- M-Switch FAB (Frequency Assignment Broadcast) providing unidirectional red to black separation.
The second class of application is for cross-domain use, following the architecture shown below.
The model is that standard protocols are mapped onto two unidirectional XML message flows that are sent through the guard. The Edge servers are responsible for ensuring that the XML messages transferred comply to the application profile. M-Guard simply enforces this.
Isode provides an XMPP Cross Domain solution, described in the Isode whitepaper [Isode’s XMPP Cross Domain Solution]
Isode plans to provide a messaging cross domain solution with a new product:
- M-Switch Edge, for messaging services. This is particularly focused on military messaging using STANAG 4406, ACP127 and SMTP, but is also suitable for general purpose messaging.
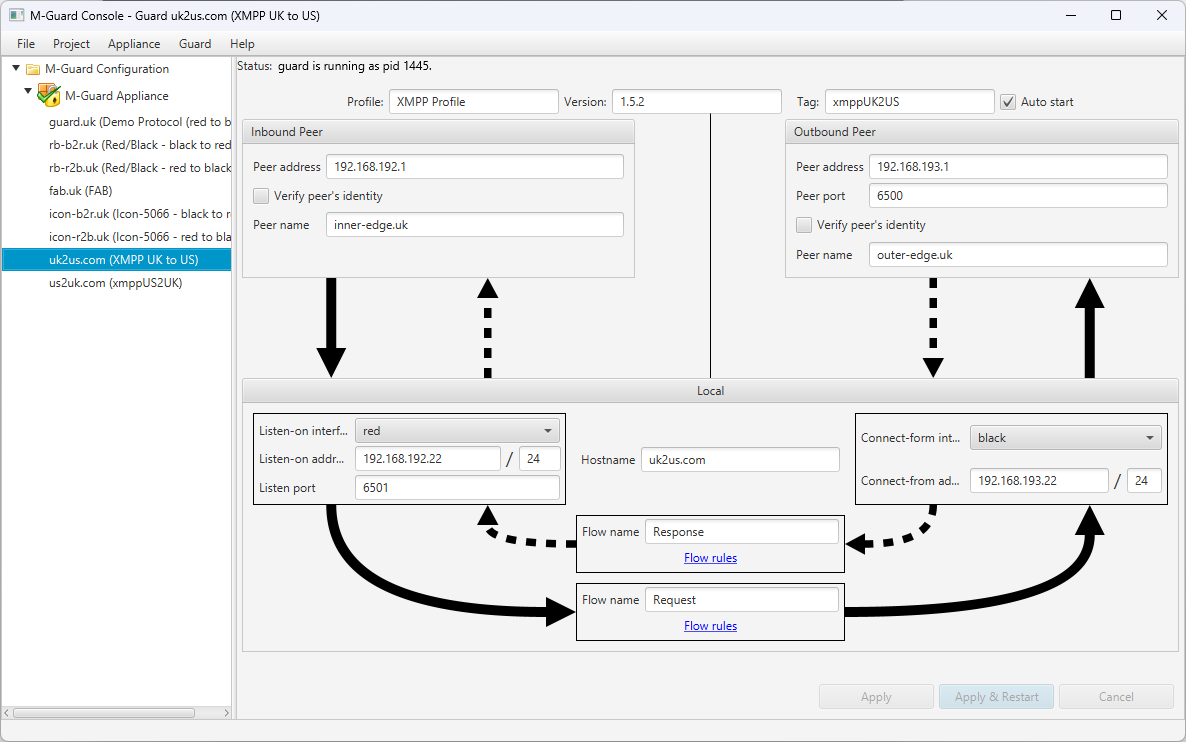
M-Guard Console is the management GUI for M-Guard, which will connect to M-Guard over a third (management) network. M-Guard Console is used to set up and configure the M-Guard appliance and M-Guard instances running on the appliance. It handles general operations and maintenance, such as system backup.
M-Guard Console uses “Projects” to describe and manage the configuration of multiple individual M-Guard instances.

The screenshot above shows use of M-Guard Console to configure a Guard instance on an M-Guard appliance. A key part of this configuration is setting up addressing to enable correct communication between M-Guard and the consuming and producing applications.
M-Guard activity can be monitored using Syslog including rsyslog (secured with TLS), which will be done on the management network. Events are sent to record activity and errors. These syslog messages can be sent to the Syslog management system of choice. The screenshot below shows M-Guard Syslog messages displayed by the free Visual Syslog Server tool.
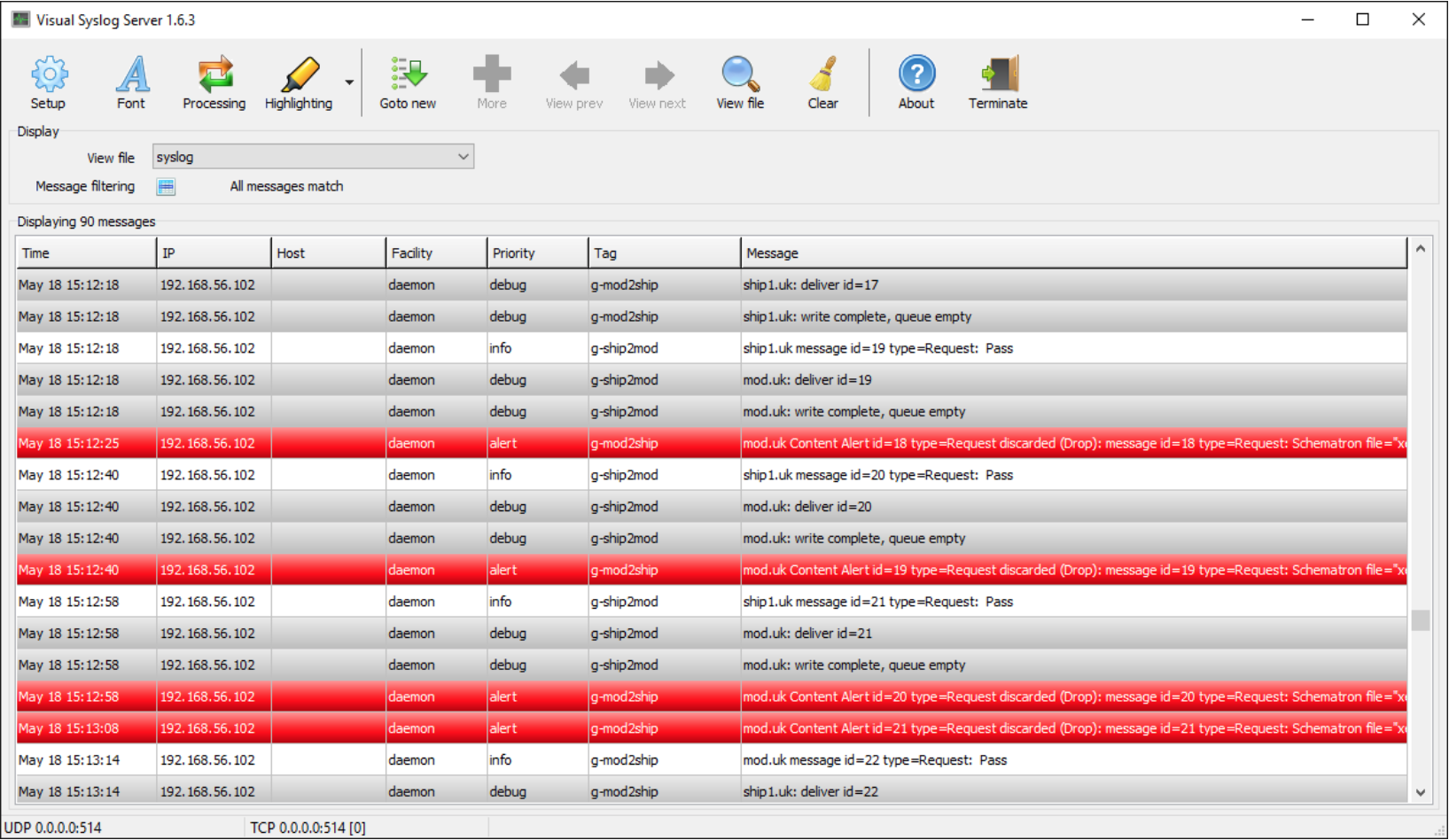
There are test Producer and Consumer applications associated with M-Guard Console; these can be run to test one or other side of an operational configuration, or (as in the configuration shown above) both run at once to test and demonstrate an M-Guard instance.
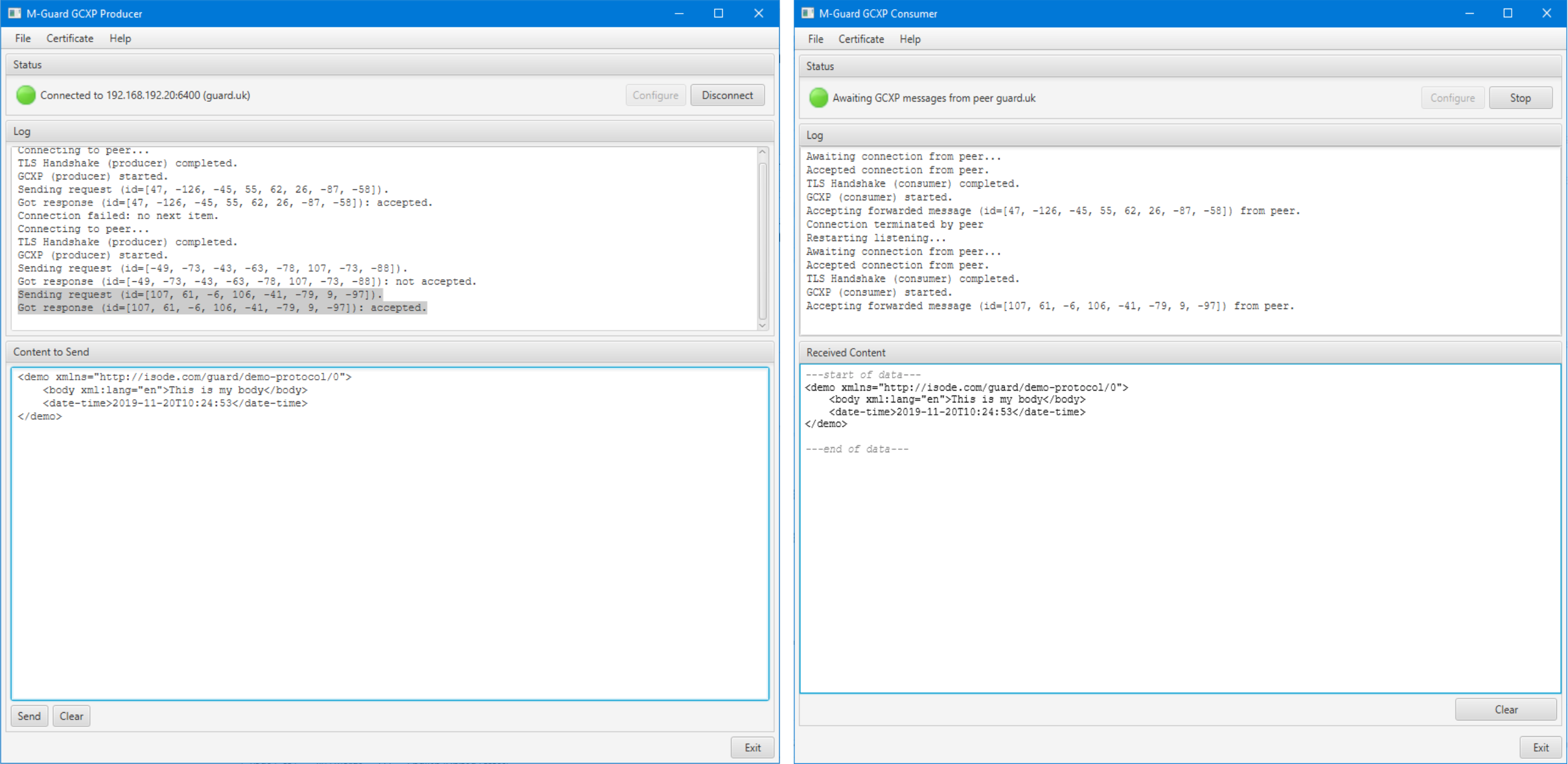
The screenshots above show the test tools sending XML messages through an M-Guard instance, which is a useful way to test and demonstrate M-Guard capability. The Producer can be used to send any XML message including selection from loadable and built in catalogs, which include basic XML stanzas, plus a set of “Demo Protocol” messages, one of which is shown above. M-Guard can be configured with rules relating to Demo Protocol, enabling easy demonstration of M-Guard capability to accept and block XML.
PKI Support
GCXP connections always run over TLS and will usually use PKI verification. Each guard instance on an appliance will run in a FreeBSD Jail (to provide seperation from other guards) and will have a PKI identity. Checking certificate validity (using CRL or OCSP) would introduce too many security risks, so is not done. A consequence of this is that in the event of certificate compromise, the whole PKI needs to be replaced. This makes use of standard PKI impractical.
To address this, M-Guard Console includes a per-appliance Certification Authority (CA). This will issue a certificate for each guard on the appliance and using standard Certificate Signing Requests (CSR) will issue certificates for the applications that connect to M-Guard.
Platforms
M-Guard instances run on a Guard Appliance, a single Appliance may run one or more Guard instances. A common set up is to have one M-Guard appliance running a pair of M-Guard instances (one in each direction). M-Guard is stateless, so that multiple M-Guards may be set up to provide a redundant configuration.
The Guard Appliance can be a virtual or physical device utilizing the NanoBSD variant of the FreeBSD operating system. NanoBSD is specifically designed for appliances and has been chosen for its small footprint and excellent security characteristics.
Virtual Appliance Platforms
Two platforms are currently supported, and others may be added:
- Microsoft Hyper-V
- Oracle VirtualBox
Physical Appliance Platforms
The guard appliance is intended for diskless hardware and is currently targeted for Intel Atom processor based appliances. The reference hardware is the Netgate 6100, we support the following versions:
We currently do not support the Netgate 6100 MAX TNSR.
We are happy to work with partners to support other hardware platforms.
Ready to request an Evaluation?
Thankyou for considering Isode’s software products. To request an evaluation, please select the product(s) you are interested in, then fill out the enquiry form.
Select your Evaluation products:
Customer Portal
For access to our customer portal please login below.
If you are having trouble accessing the portal, please contact our support team who will be happy to help.
Need help with your account? Contact us
