Industries
Military
Through a combination of direct relationships and our global partner network we provide secure communications solutions to military forces all over the world. We have been working alongside NATO and other organisations for more than 25 years, developing open standards software that works with whatever systems are currently in place, keeping military forces one step ahead at all times.

Our approach
Isode is a close, long-standing partner of government authorities, armed forces and leading companies in the defence industry.
Through a combination of direct relationships and our global partner network, we provide a number of solutions specifically developed for the military. Delivering secure communications options within even the most complex, and challenging environments.
Military Messaging
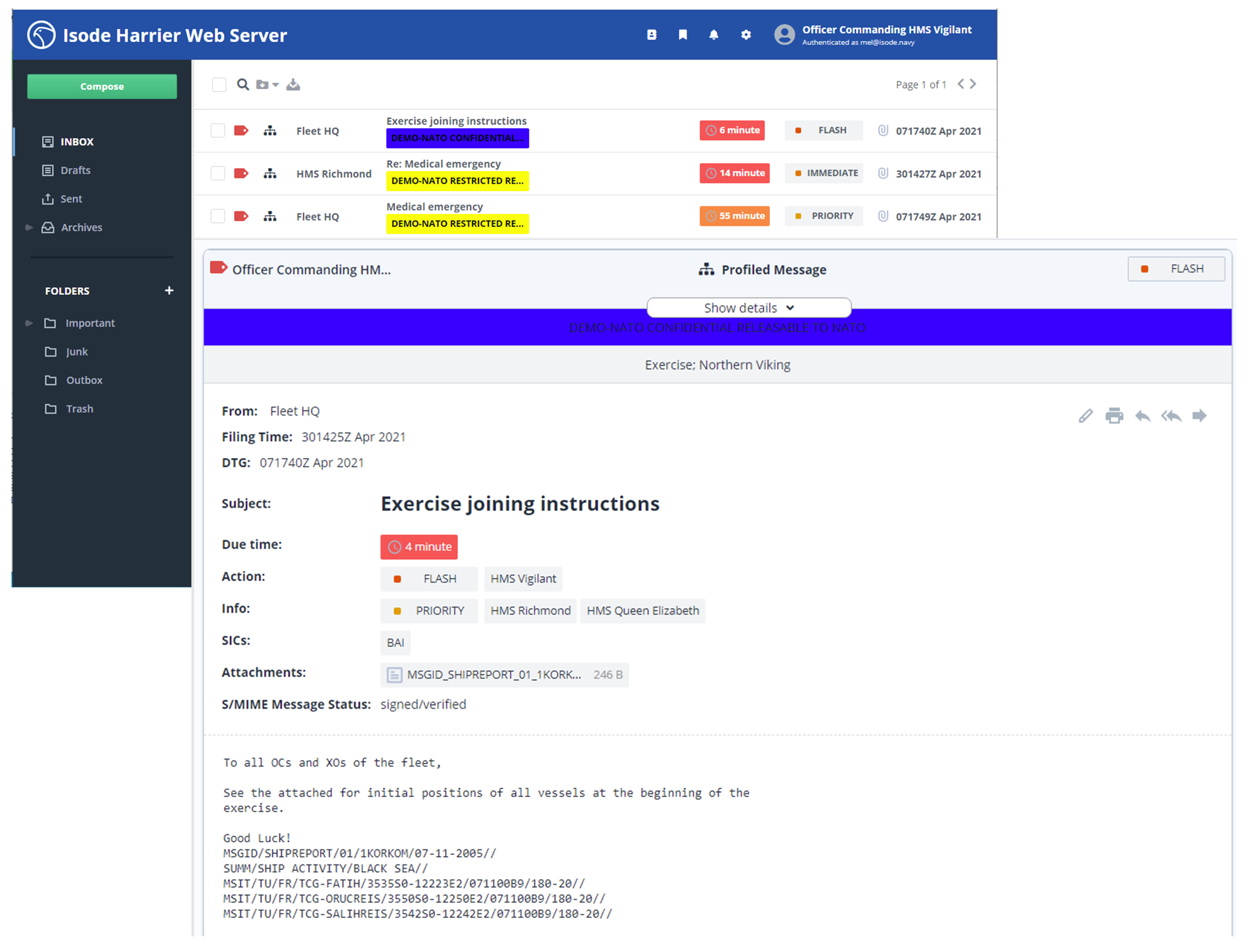
Isode provides the products needed for a complete high functionality Military Message Handling System (MMHS) system.
This includes a Web Client and server support for STANAG 4406, ACP127 and SMTP protocols, including gateways between these protocols following ACP145 and MIXER. Isode products are ideal for deployment on high speeds networks, over HF Radio and in other degraded and constrained bandwidth environments.
XMPP Chat
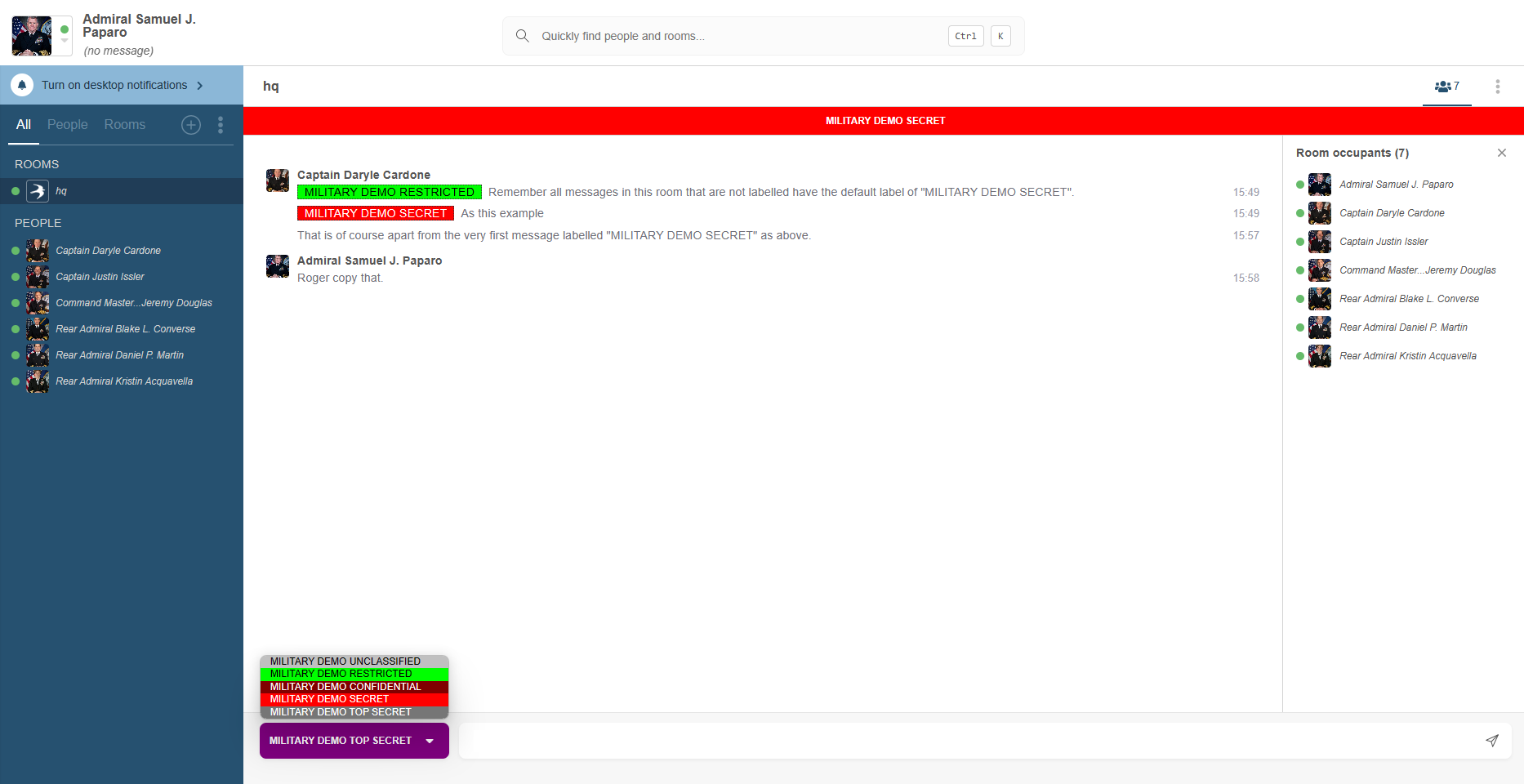
Isode provides XMPP server, gateway and client products ideally suited to military deployments.
Whether you’re just looking for a capable XMPP chat client, or you’re after a full, secure XMPP Solution we are able to provide everything a modern military needs. Our XMPP solutions are used by military organisations across the world and are capable of deployment over both standard internet networks and constrained networks.

HF Radio
HF Radio is an important element of military communication, providing support in Denied Degraded Communications and Control Environments (D2C2E) and is the only practical alternative to SatCom for Beyond Line of Sight (BLOS) communications.
We provide a full suite of products specifically designed to transform a standard HF Radio network into a highly capable, and effective, communication tool. Capable of operation using Chat, Email and other IP Applications.

NATO BRASS
NATO provides an expansive network of HF stations, delivering coverage for HF radio communications to naval forces across the world. What makes this so effective is the adherence to open standards and set system configurations. Relying on programmes such as BRASS (Broadcast and Ship to Shore) to provide this.
Our BRASS Solution uses our open standards based products to deliver the key elements to the NATO BRASS systems. Providing modern, scalable communications technology to naval deployments.
Isode provides the products needed for a complete high functionality Military Message Handling System (MMHS) system.
This includes a Web Client and server support for STANAG 4406, ACP127 and SMTP protocols, including gateways between these protocols following ACP145 and MIXER. Isode products are ideal for deployment on high speeds networks, over HF Radio and in other degraded and constrained bandwidth environments.
ACP 127
ACP127 is a text based protocol for formal military messaging. M-Switch provides full support for ACP127 and related military protocols, including ACP126, ACP128, JANAP128 and DOI103S. This includes gateway capabilities to SMTP and STANAG 4406. Isode also provides full support for operation over HF Radio and in particular for BRASS (Broadcast and Ship to Shore) deployments. More details can be found on the M-Switch ACP127 add-on page.

STANAG 4406
STANAG 4406 is the NATO Standard for formal military messaging. Used for both Strategic and Tactical messaging, STANAG 4406 has a number of special protocols to support tactical messaging, in particular to support very low bandwidth links such as HF radio (STANAG 4406 Annex E) and to support receivers in Emission Control (EMCON) mode who can receive but not send data.
Isode’s M-Switch X.400 is fully compliant to the STANAG 4406 standards and architecture and can additionally be configured as a gateway to all other messaging standards supported by M-Switch X.400 and M-Switch STMP.
ACP 145
National variants of military messaging protocols have led to a situation where interoperability between national MMHS systems is not guaranteed. ACP145 has been defined in order to overcome this problem, and is a complete protocol definition for international inter-working. The ACP145 specification has led to a requirement for “ACP145 gateways”, which convert between the national variants of MMHS and ACP145. M-Switch MIXER, alongside M-Vault (an ACP133 Military Directory) can be deployed as an ACP145 Gateway, and including support for Security Labels and Message Digital Signatures.
Use of M-Switch MIXER also enables national networks using SMTP and S/MIME to be connected using ACP145. Further details can be found in the Isode whitepaper [ACP145: Isode Support of International MMHS Gateways].
MMHS Over SMTP
Full military messaging can be provided over the widely used and industry standard SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) protocol. SMTP infrastructure can be shared between MMHS and informal email, reducing management overheads and to support communities where only partial MMHS capability may be required, or communities where a small subset of users require MMHS capability, without the requirement of deploying a separate MMHS infrastructure.
M-Switch SMTP features support for the wide range of Open Standards necessary to deliver military messaging over SMTP, including:
- RFC 6710: SMTP Extension for Message Priorities
- RFC 6477: Registration of MMHS Header fields for use in Internet Mail
- RFC 7444: Security Labels in Internet Mail
- RFC 8494: Multicast Email (MULE) over Allied Communications Publication (ACP) 142
This is described in the whitepaper [Military Messaging (MMHS) over SMTP].
Message Profiler
The M-Switch Profiler enables messages to be delivered to recipients based on message content, a capability often required as part of a military messaging solution. The M-Switch Profiler is a high functionality profiler which addresses NATO and other high-end profiler requirement sets and operates directly onthree stadard military messaging protocols:
- SMTP with RFC 6477 (part of M-Switch SMTP)
- STANAG 4406 (part of M-Switch X.400)
- ACP 127
Compressed File Transfer Protocol (CFTP)
Isode recommends ACP 142 use for constrained bandwdith messaging but, for those customers who would prefer not to implement ACP 142, M-Switch Constrained Network products support CFTP (sometimes nown as BFEM/Battle Force E-Mail). More information on CFTP and other constrained bandwidth protocols can be found in the whitepaper [Messaging Protocols for HF Radio].
Harrier MMHS Client
Harrier is Isode’s web based military messaging client. Developed from the ground up with the needs of military messaging in mind, Harrier brings a modern user interface to military messaging and can be deployed as part of a solution using any of the messaging protocols supported by Isode’s M-Switch family of MTAs and Gateways.
Harrier provides all of the features needed for MMHS, including Security Labels, Action/Info Priority, DTG, Reply-By, Expires, Processing Time Warning, SICs (Subject Information Code), Message Type, Handing/Message Instructions, Digital Signature using S/MIME, Encryption using S/MIME Triple Wrap and Draft and Release.

MMHS Server Capabilities
The M-Switch server and associated management tools provide a number of capabilities available for all protocols:
- Security Label Access Control. Security labels extracted from any of the supported protocols can be used to control delivery and routing.
- Security Label Conversion. Security labels can be converted between different formats and policies.
- Digital Signature and Encryption Conversion. Messages can be signed at the boundary to support protocol conversion and transfer between different security domains.
- Message Tracking. Supports end to end tracking based on delivery reports and read receipts.
- Message Vetting.
- Message Correction in support of “Fire and Forget”.
- Message Distribution, including: STANAG 4406 Distribution Lists; SMTP Distribution Lists; ACP127 AIGs and CADs; Military Address Lists.
- Operational Statistics.
- Alerts to show local and remote operators when messages are delayed or components need attention.
- Operator Support. GUI support for Message Operators, which is important for support over slow and unreliable networks, and is particularly important where ACP 127 is used.
HF Radio Support
M-Switch contains specific support for HF Radio, in particular to support the NATO BRASS environment as described in [Isode’s Solution for BRASS (Broadcast and Ship to Shore)].
Isode recommends the ACP 142 protocol described in [ACP 142: SMTP & STANAG 4406 Messaging for Constrained Networks], which gives efficient multicast and EMCON support. ACP 142 is used in NATO BRE1TA. Other HF messaging protocols are described in [Messaging Protocols for HF Radio].
Apart from some BRASS protocols, these protocols operate over STANAG 5066 and may use Isode’s Icon-5066 is a modem-independent STANAG 5066 server. STANAG 5066 provides a link layer optimized for HF Radio and described in the whitepaper [STANAG 5066: The Standard for Data Applications over HF Radio].
Constrained Network Environments
Isode’s MMHS products have a range of capabilities to support Denied Degraded Communications and Control Environments (D2C2E), which includes but is not limited to HF Radio. M-Switch supports efficient operation over a range of networks, including EMCON support.
Isode’s core approach is to provide optimized server-to-server communication, as this enables maximum efficiency to be obtained from the underlying networks, and isolates clients from those underlying networks. This allows use of standard clients, as specialized functionality is provided by the servers. Clients can connect directly to the Isode servers, or indirectly via other servers.
Isode provides XMPP server, gateway and client products ideally suited to military deployments over both internet quality networks and constrained networks.
What Isode Provides
- M-Link User Server: Robust and scalable XMPP server with features important for military deployment.
- IRC Gateway: Gateway between XMPP Multi-User Chat rooms and Internet Relay Chat (IRC) Channels.
- XMPP Boundary Guard: M-Link Edge allows for the application of boundary controls on cross domain traffic, either independently or in conjunction with a High Assurance Guard.
- XMPP Messaging for Constrained Networks: Isode’s XMPP products for constrained network operations enable efficient use of 1:1 and multi-user chat over HF and SatCom networks.
- Forms Discovery & Publishing: Publishing, share and subscribe for structured forms (such as MEDEVAC).
- XMPP Client: Swift multi-platform XMPP client.
Instant Messaging is becoming an increasingly important communication option militaries, particularly for sharing communication with a large number of users with Multi-User Chat capabilities. Voice and video communications are often impractical due to networking constraints and/or operational characteristics. Email or formal messaging are often too slow and cumbersome where information sharing and associated decision making need to happen very quickly.
M-Link User Server
Isode’s M-Link User Server is a robust and scalable XMPP server for use over standard quality network links. Isode has incorporated into all M-Link products features that make them the natural choice for instant messaging and presence in military, intelligence and government deployments. These features include:
- Security labels according to XEP-0258: Security Labels in XMPP.
- Windows SSO.
- Strong Authentication (based on X.509 Public Key Infrastructure).
- Clustering to provide resilience against node and site failure.
- Short and long term message archiving and archive search.
XMPP Client

Swift, is a modern web chat client, designed to be used anywhere, on any device. It enables you to deploy a high capacity, secure chat solution across your network with zero footprint deployment.. Swift contains many features which make it ideal for use in secure environments, including:
- Security labelling of messages and MUC rooms.
- Message delivery acknowledgements.
- Strong authentication, which can be used with smart cards.
- HTTP File Upload & Transfer
- Custom alerts and colour coded highlight rules based on keywords and sender.
XMPP/IRC Gateway
The M-Link IRC Gateway functions as a gateway between XMPP Multi-user chat rooms and IRC channels. The Gateway server uses the IRC client to server protocol to connect to IRC, in order to maximise interoperability with different IRC servers. Connections to IRC channels are totally transparent to XMPP MUC users with no downgrade of security for XMPP users. Security label support is retained with translation to IRC users as FLOT (First Line of Text) labels in IRC messages.
For more information, see the product page on the M-Link IRC Gateway and the whitepaper [Interconnecting XMPP and IRC].
XMPP Boundary Guard
Standard XMPP deployment assumes Internet-like direct connectivity with all servers. Military deployments typically need boundary and cross domain protection to work with partners. Isode’s M-Link Edge product provides this capability for XMPP either operating on its own or in conjunction with a High Assurance Guard.
M-Link Edge can validate, constrain and transform the XMPP messages it handles. M-Link Edge enables boundary controls to be completely independent of the core XMPP service and, as a boundary service provided by M-Link Edge, can support multiple XMPP servers within an organisation.
XMPP Messaging for Constrained Networks
Many military deployments will use network links with poor and variable quality. High latency is a particular problem for XMPP deployment, because of the requirement to avoid handshaking. Two M-Link products are specifically designed to overcome the issues of working in such environments; M-Link Constrained Network Server and M-Link Constrained Network Gateway.
Product capabilities for constrained networks are described on the product page for these two products as well as in the whitepaper [Operating XMPP over HF Radio and Constrained Networks]. They include:
- Stream Compression.
- Roster Versioning.
- Presence Stripping.
- Optimized Server-to-Server Protocol.
Forms Discovery & Publishing
Forms are widely used in military operations, where there is a need to handle forms (such as Medical Evacuation or “MEDEVAC” forms) quickly and share completed forms with a large number of parties who may need to take action, such as helicopter services, emergency vehicles and medical facilities.
Both the M-Link User Server and M-Link Constrained Network Server enable flexible Forms Discovery and Publishing (FDP) using the protocol described in XEP-0346. FDP provides a mechanism to allow M-Link to store a list of Topics and associated form templates that can be retrieved and completed by an FDP-aware client. Once the completed form is submitted back to the Server, interested parties who have subscribed to the Topic will be immediately notified that a new instance of the form has been completed.
For more information on FDP, see the products page on XMPP Forms Discovery & Publishing and the whitepaper [Military Forms using XMPP].
Directory services are a critical military component, used for tactical and strategic systems. Military directories, standardized in ACP 133, are used to provide information services, support of military messaging, and as supporting infrastructure for other applications such as PKI (Public Key Infrastructure).
What Isode Provides
- Directory Server: The M-Vault directory server (see the main product page for an overview) is the core component of Isode’s offering for military directory, providing:
- Directory Synchronisation with partner organizations using Sodium Sync.
ACP 133 Conformance
Conformance is critical for military directories. The primary definition of military conformance is ACP (Allied Communication Publication) 133 “Common Directory Services and Procedures”. ACP 133 is based on the ISO/ITU X.500 Directory Standard, and makes use of X.500 protocols for replication and directory management. LDAP, the Internet Standard Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is also based on X.500, and is generally the preferred protocol for military clients and military applications to read data from an ACP 133 directory. Data updates are usually done using X.500 DAP, as this offers additional security features. Further information on the ACP 133 directory is provided in the Isode white paper [ACP133: The Military Directory Standard].
Directory Security & Strong Authentication
Security features are an important element of ACP 133 directory. Strong authentication and related capabilities using digital signatures are central to directory security. All of the directory protocols used by M-Vault make use of digital signatures based on X.509 PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) to provide peer authentication and signed operations.
Complementing the PKI based authentication and signed operations, Isode provides a number of important security features including:
- Access Control. X.500 gives flexible access control that is used in conjunction with authentication to control access to and update of data.
- Security Label based access control, described in the whitepaper [Using Security Labels for Directory Access Control and Replication Control].
- Audit Logging. Isode provides detailed audit logging, which is important for a secure environment.
Replication & Distribution
A key benefit of using a directory is that data can be highly distributed. In a commercial environment, distribution is primarily used to optimize performance and to avoid single point of failure. In a military environment, there are more stringent resilience requirements, and it is critical that local systems have minimum external dependencies. This leads to four key points about the structure of a military directory:
- Chaining (protocol connection between two directory servers), using X.500 DSP (Directory System Protocol), is often not used. Directory servers are configured to either return data or to pass responsibility back to the client.
- Need to always have a directory. Applications and users that require directory access should not have to rely on availability of a remote directory. This will generally mean that a military deployment will use a larger number of servers than a commercial one, in order to provide servers at all locations.
- Data is highly replicated, using X.500 DISP (Directory Information Shadowing Protocol). The goal is to ensure that all data required is held in the local server. This means that military directories will generally make extensive use of replication.
- Security. Replication must be secure, and the strong authentication and signed operation capabilities of DISP make it ideal.
A simplistic interpretation of this approach would lead to all data in all servers. There are two reasons why this is not done in practice:
- Need to know. Data on people and resources should not be replicated onto servers where there is no requirement for users to have access to that data.
- Bandwidth and resource constraints. Often servers will be connected with slow links. It is undesirable to spend resource on replicating data which is not needed on the remote server.
X.500 DISP provides capabilities, which make it straightforward to provide selective replication and meet these two requirements. This includes attribute filtering (to remove attributes not needed), and “chop”, which enables entries and parts of the directory information tree to be selectively replicated. This is a powerful part of the X.500 architecture, which is useful for building a military directory, and is implemented in M-Vault.
Some military directory deployments have suggested use of directory synchronization products (meta-directories) to achieve complex replication scenarios. These techniques generally use LDIF (LDAP Data Interchange Format), which relies on common interpretation of string formats, which may not be standardized. Isode believes that this approach adds unnecessary complexity and will reduce robustness and security. Isode strongly recommends use of advanced X.500 DISP replication to build robust replicated directory deployment using open standards.
Further information on use of X.500 DISP for replication to meet military requirements is discussed in the Isode whitepaper [Building a Highly Replicated Directory: The case for X.500 DISP].
M-Vault provides a failover capability to provide live backup for a master directory. This is described in [M-Vault Failover and Disaster Recovery].
Finally, M-Vault provides for a multi-master capability. This provides benefits in many scenarios and is described in [ACID Multi-Master Replication in M-Vault Directory].
Directory Synchronization
While directory synchronization is not the best choice for core directory replication, it is an important part of many military directory deployments, due to the need to integrate data from multiple directories and to support LDAP directories that do not support open standard replication.
Where there is a need to share directory information with partner organizations, or to integrate information from systems that do not support ACP 133 and X.500 DISP, Sodium Sync provides flexible data sharing. This includes synchronization by email and over air gap as described in [Directory Replication by Email and over Air Gap].
Client and User Access
Client protocol access to a military directory may use either X.500 DAP or LDAPv3. M-Vault supports both of these protocols. For applications that make updates to the directory, Isode recommends use of X.500 DAP, using strong authentication and signed operations. This approach, with its security benefits, is supported by all Isode tools that modify data in the directory.
LDAP is widely supported in many applications and LDAP provides good functionality to access the directory, provides data confidentiality (using Transport Layer Security (TLS)), and gives a range of authentication mechanisms, including strong authentication when used in conjunction with Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL). For applications that only read data from the directory, LDAP is generally a good choice.
HF Radio is an important element of military communication, providing support in Denied Degraded Communications and Control Environments (D2C2E) and is the only practical alternative to SatCom for Beyond Line of Sight (BLOS) communications.
Solutions for HF Radio require specialized capability at every layer from antenna to application. Isode provides the upper layers, which can be used with hardware from multiple vendors, enabling Isode partners to provide a complete solution.
What Isode Provides
Isode seeks to provide “everything above the modem”, comprising a set of software products including applications, layer services and management:
- STANAG 5066: The protocol layer between modems and applications.
- Messaging: Formal Military Messaging (MMHS) and email optimized for operation over STANAG 5066.
- XMPP: Instant Messaging and Presence services optimized for operation over STANAG 5066.
- IP Services and Web Browsing: Generic provision of IP Services over HF and, in particular, web browsing.
- Directory: Optimized replication of directory services over HF links.
- HF System Management: Management tools to provide integrated control and monitoring of Isode and “lower level” components.
STANAG 5066
STANAG 5066 is the NATO standard HF link layer, which sits between modems and HF applications. Icon-5066 is Isode’s STANAG 5066 server that provides this layer in a modem-independent manner. Modems from Collins and RapidM are currently supported. Icon-5066 provides support for Wideband HF (WBHF) and the associated 4G ALE standard.

Messaging
Isode provides a complete solution for Military Messaging (MMHS) which includes ACP127 and BRASS support over HF, as well as modern BR1ETA, ACP142, and STANAG 4406 operating over STANAG 5066. The messaging solution includes server components for email, with a choice of protocols for use over STANAG 5066.

XMPP
Isode’s market leading Military XMPP solution provides full chat and presence capabilities that can be used with the Isode Swift client of NATO JCHAT following the NATO standards for chat. Isode’s XMPP servers operate efficiently over STANAG 5066 and provide Federated Multi-User Chat (FMUC) using XMPP Standards Foundation protocols.
IP Services & Web Browsing
sode’s Icon-PEP product provides IP services over STANAG 5066 with an optimized HF Performance Enhancing Proxy protocol to provide good performance and resilience for TCP. Icon-PEP can be used to support Web Browsing over HF, which provides a “pull” service for mobile units, to complement the “push” services provided by XMPP and Messaging.
HF System Management
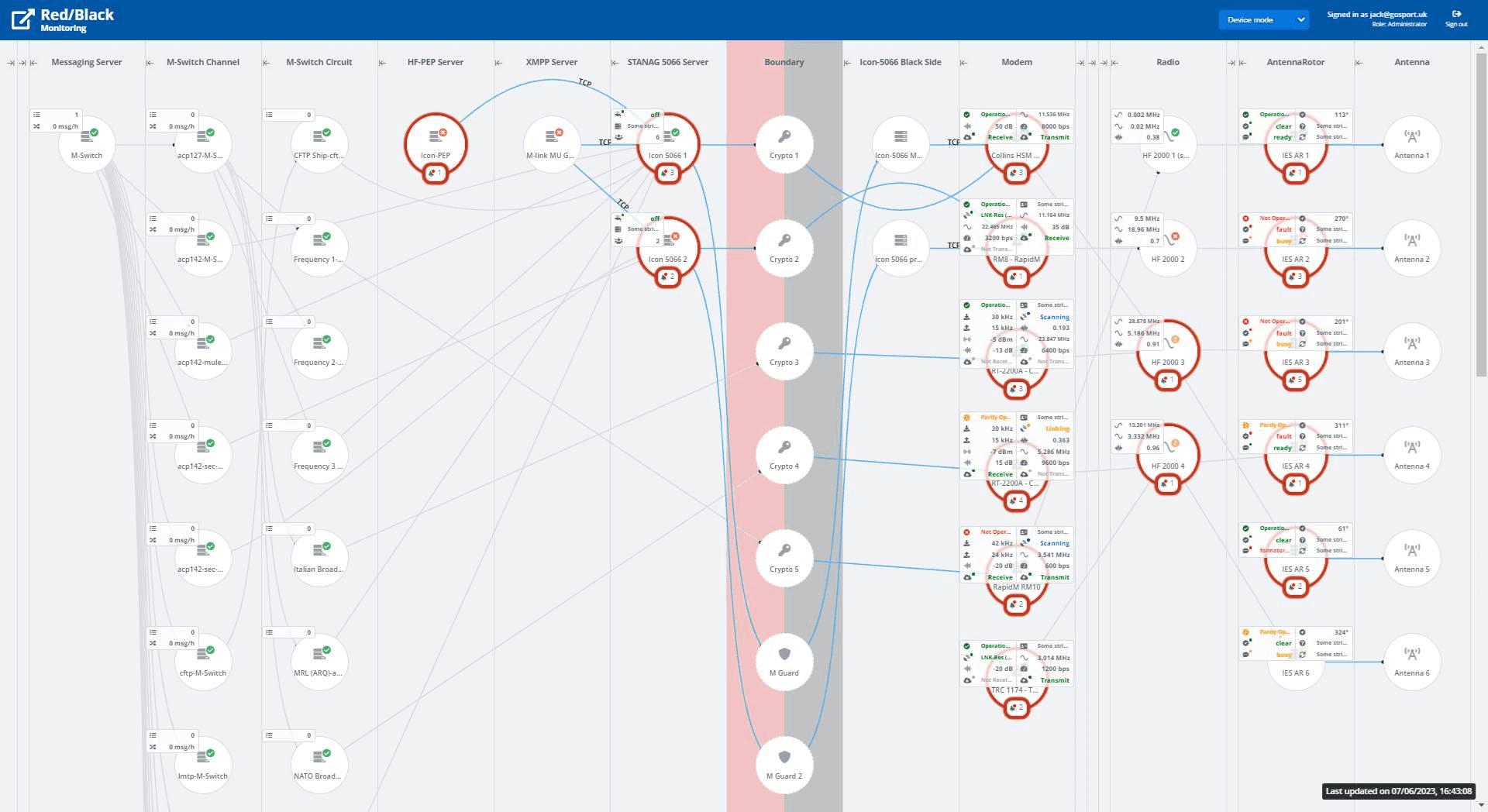
HF Systems need a communication chain with specialized components from antenna to application. Those components need to be monitored and controlled in a coordinated manner. This is complicated in many deployments, because some components sit “black side” and others “red side” with security considerations across the red/black boundary.
Isode’s Red/Black product provides control and monitoring of both Isode provided components and of third-party “lower layer” components using an extensible driver mechanism.
Mobile Unit Mobility
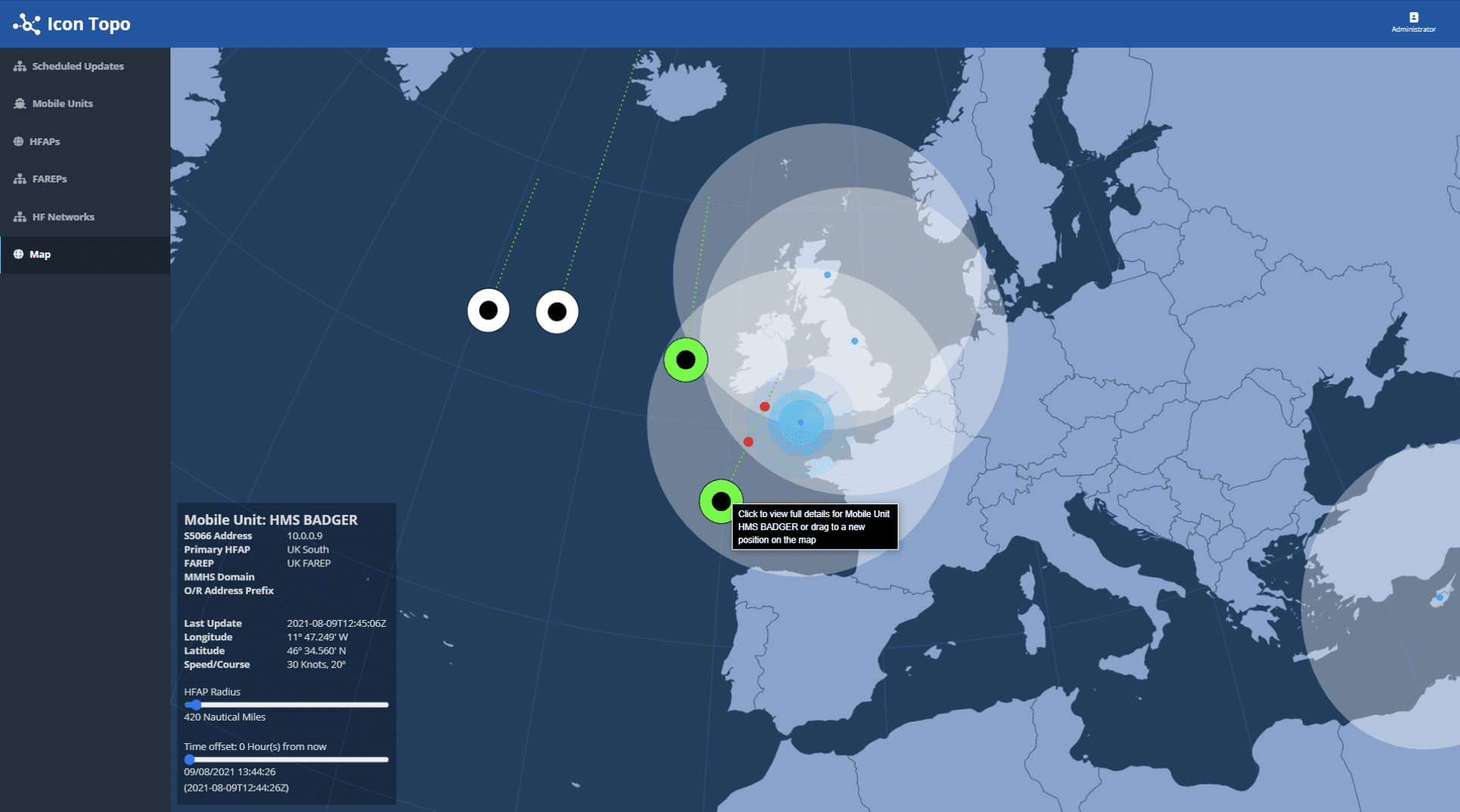
When a ship or other mobile unit (MU) uses a HF connection you want to be sure that as it goes through its planned route that connection isn’t lost. Icon-Topo provides a way to monitor the location of MUs as they traverse across your HF network, scheduling the transfer of communications from one access point to another. Ensuring that the MU doesn’t lose connection as it carries out its duties.




Lower Level Components
HF communication needs a number of components that Isode does not supply, such as modems, radios, power amplifiers and antennae. Isode products interface at two points:
- Modems, noting that in modern systems modems are often integrated with radios as a single combined unit with independent data and control interfaces.
- ALE (Automatic Link Exchange) Units. ALE capability is often integrated with modems, but the control is considered independent.
Data interfaces to modems follow open standards and so this interface is modem independent. ALE and modem control interfaces are proprietary, and is need vendor specific integration.
NATO provides an expansive network of HF stations, delivering coverage for HF radio communications to naval forces across the world. What makes this so effective is the adherance to open standards and set system configurations. Relying on programmes such as BRASS (Broadcast and Ship to Shore) to provide this.
Our BRASS Solution uses our open standards based products to deliver the key elements to the NATO BRASS systems. Providing modern, scalable communicatons technology to naval deployments.
We work closely with our global partners to create an extremely capable, integrated and open standards based solution to the NATO BRASS programme. We provide everything beyond the modem, while we let our partners deliver the hardware, letting us work with the most suitable people to fit the specific project requirements.
Our BRASS solution is quite an expansive one, and utilises almost our entire software suite. Detailed in the diagram below, eveything in blue covers the standard requirements, while everything in red is additional capability that we provide to enhance the solution.
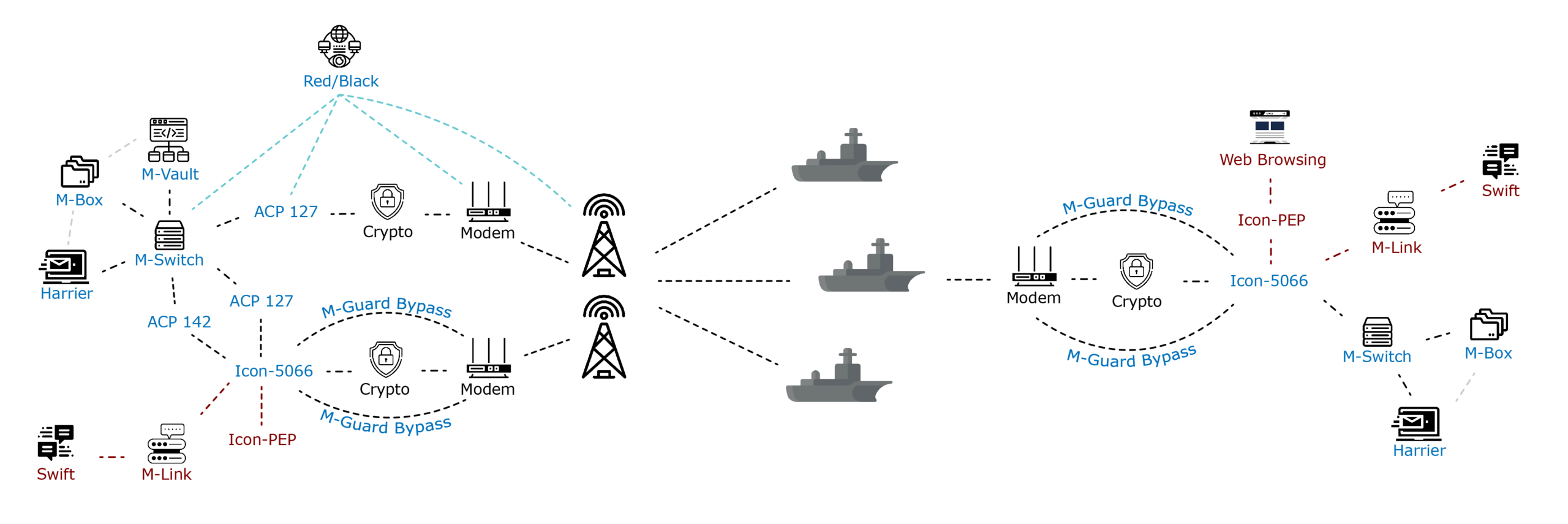
M-Switch
M-Switch is a message switch capable of operating over both high-bandwidth, stable connections and low-bandwidth connections such as HF Radio. It is used in conjunction with M-box and M-Vault (see below) to provide the back-end systems for Isode’s Military Messaging solution. This messaging server is central to both BRE1TA email and military messaging services. M-Switch supports:
- SMTP for email links (BRIPES T-Mail service)
- STANAG 4406 for military messaging
- ACP 127 broadcast including FAB, OTAM and Ship to Shore
- ACP 127 over COSS (STANAG 5066 Annex P) (for Maritime Rear Links)
- STANAG 4406 Annex E (Military Messaging over HF following STANAG 5066 Annex Q)
- Email over HF following CFTP (STANAG 5066 Annex V) and MULE (RFC 8494 and STANAG 5066 Annex Q)
- Military Message Profiling.
M-Box
A high-performance message store that supports IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) and POP (Post Office Protocol). It provides the message storage and access component for both email and military messaging. M-Box is designed to be flexible in its configuration, and is built with an architecture that enables mail boxes to access multiple servers instead of being locked to a specific server, simplifying management and facilitating scalability.
M-Box, like all Isode products, is built with an Open Standards approach in mind, and has a long list of standards conformity. For the full conformance list you can view the M-Box product page.
M-Vault
A secure LDAP/X.500 server capable of acting as a standalone directory server, as part of a distributed directory service, or to store the configuration and/or user authentication information for Isode messaging products. M-Vault is fully compliant with the NATO Standard for Military Messaging (ACP 133) and can therefore be used in support of ACP 127, ACP 145, and STANAG 4406 messaging.

Harrier
A Military Messaging Client that provides a modern, secure web UI and supports SMTP, STANAG 4406 and ACP 127. Harrier allows authorised users to access role-based mailboxes and respond as a role within an organisation rather than as an individual.
Harrier provides a number of unique features designed for Military Messaging including draft-and-release message approval process, the option to assign security labels based on both NATO and home country security labelling, and integration with Systematic’s IRIS forms product which provides pre-built message templates based on SICs.
M-Link
Our core instant messaging and presence server, based on the XMPP (eXtensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) standard supported by NATO. M-Link provides an array of security features to manage and control the instant message communications sent between users of an XMPP Chat Client with configurable rules including Security Labelling at both the individual message and multi-user chat (MUC) room level.
M-Link supports the BRIPES T-Chat service. For use in a BRIPES system, three different configurations of M-Link are required:
- M-Link MU Server: Server to run on Ship (Mobile Unit) offering XEP-0365 over STANAG 5066 optimized communication to shore.
- M-Link MU Gateway: Shore server to communicate with ships using XEP-0365.
- M-Link User Server: Server to provide shore side user service.
Swift
An XMPP chat client. It can be deployed as either a desktop client or a web-based application. Both options support 1:1 Chat, MUC rooms, Presence and Roster indications and Security Labelling. Swift is built in conformity with a long list of Open Standards which is available within the Swift product page
Icon-5066
A modem-independent STANAG 5066 Server, supporting STANAG 5066 Ed4. Used as a Link-Layer application, it provides a link between software and hardware in an HF network and enables the use of applications over HF Radio. Like all Isode products, it is designed with interoperability in mind, working with any capable hardware regardless of vendor. The Icon-5066 UI is a web-based application that enables configuration and monitoring of variables like Transmission SNR, Modem Status, Error Rate for transmissions and ALE Status.
Icon-PEP
Enables the deployment of IP applications over HF Networks, using STANAG 5066 as the network interface. Icon-PEP can provide this in two ways:
- Generic switching of IP packets over an HF network, causing it to act as an IP subnet. This enables support of IP applications.
- Optimised support for TCP over IP using a Performance Enhancing Proxy (PEP) to optimise TCP performance over HF.
This enables a wide range of applications, such as web browsing, to operate over HF. It is currently used to provide the BRIPES T-Web service of MU (Ship) Web access to shore services
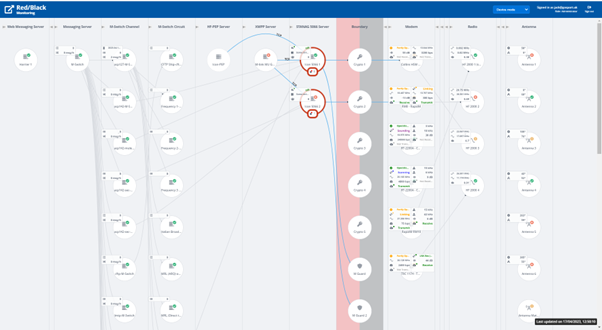
Red/Black
A system-management tool for monitoring and controlling HF Communications Chains, including operation across red/black secure network boundaries. It is a web-based server intended to complement the primary device monitoring tools in place across a network.
A full technical description of Red/Black can be found here
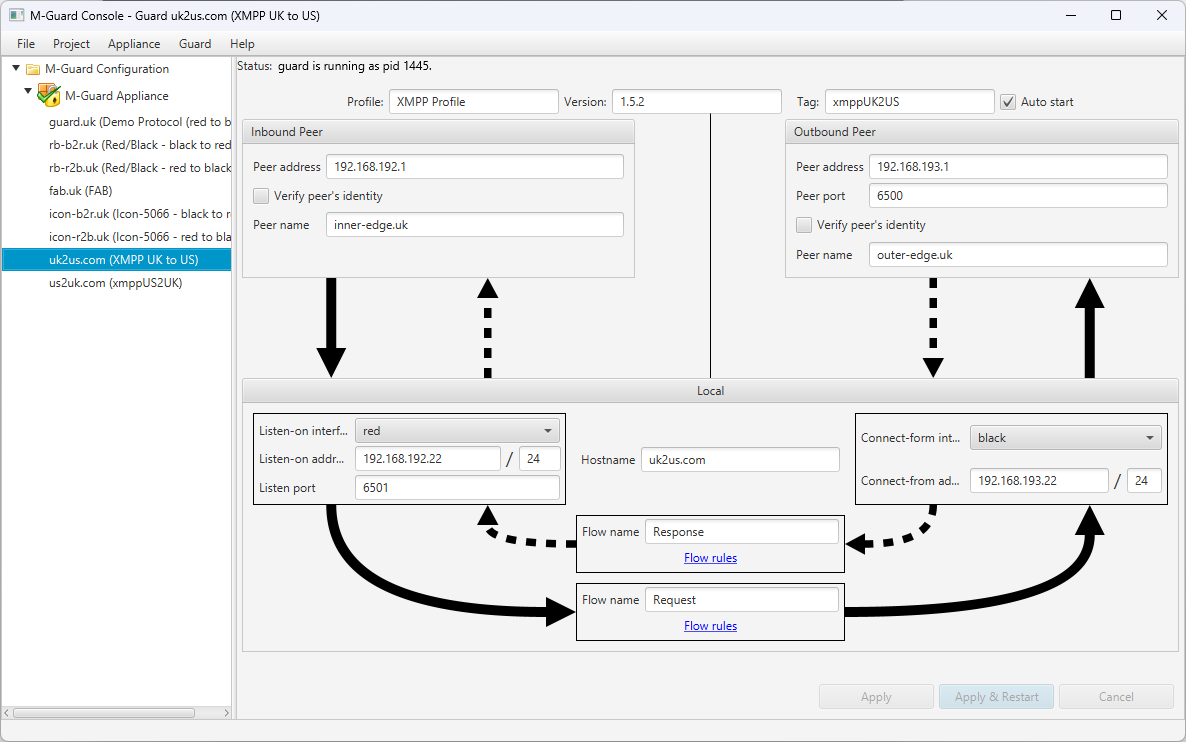
M-Guard
An XML guard that is used at a network boundary to control traffic. It performs checks against inbound XML messages and either passes or blocks them, depending on configurable rules put in place. M-Guard is used as the data isolator in support of Red/Black separation, Icon-5066 Crypto bypass and Frequency Assigned Broadcast (FAB) alongside M-Switch.

Icon-Topo
Icon-Topo enables operators to schedule MU (ship) movements between HF Access Points (HFAPs) via a web application. It ensures that as an MU moves from one location to another communication is not disrupted or lost as the MU transfers from one HFAP to another.









Ready to request an Evaluation?
We welcome evaluations of our products and will make support resources available to you for the duration of your evaluation.
Customer Portal
For access to our customer portal please login below.
If you are having trouble accessing the portal, please contact our support team who will be happy to help.
Need help with your account? Contact us
